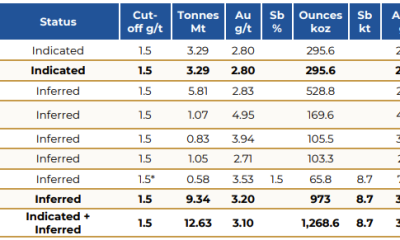
Energy & Critical Metals
Hyundai Motor to invest $85B over next 10 years to accelerate transition to smart mobility provider
At an Investor Day event in Seoul, Hyundai Motor said that it will accelerate its transition toward becoming a smart mobility solution provider by securing…

At an Investor Day event in Seoul, Hyundai Motor said that it will accelerate its transition toward becoming a smart mobility solution provider by securing a large-scale investment of KRW 109.4 trillion (US$85 billion) over the next 10 years, including KRW 35.8 trillion (US$27.8 billion) for electrification. The company aims for 2 million units in annual EV sales by 2030.
Furthermore, in order to secure leadership in the future mobility industry, it has decided to focus on future businesses, such as autonomous driving, hydrogen, robotics and advanced air mobility (AAM).
The key parts of the company’s strategy include introducing a next-generation modular architecture for EVs, strengthening EV production capacity, battery development capabilities and future businesses.
New EV platform. President and CEO Jaehoon Chang explained how the company’s second-generation dedicated EV platform, under the new Integrated Modular Architecture (IMA), will replace its Electric-Global Modular Platform (E-GMP) going forward.
The next-generation platform will be used on 13 new dedicated EV models from Hyundai Motor Group’s automotive brands Hyundai, Kia and Genesis through 2030. With IMA, the company expects to standardize modules and parts between the models to further expand economies of scale and significantly reduce EV development complexity and costs.
The vehicle development system implemented by the IMA represents a significant advancement compared to the current system, enabling maximum cost reduction through economies of scale. In the existing system, auto parts can only be shared among vehicles that share the same platform. However, with the IMA development system, over 80 common modules can be utilized across different segments, irrespective of vehicle type, allowing for versatile combinations. This breakthrough allows for greater flexibility and efficiency in the development process, paving the way for significant cost savings.
In the second-generation platform, the scope of vehicle development extends beyond the mid-sized SUVs covered by the current E-GMP system. It encompasses nearly all vehicle classes, ranging from small and large SUVs to pickup trucks, along with the flagship models of the Genesis brand.
Hyundai Motor plans to apply a range of battery solutions, including next-generation NCM batteries and LFP batteries, for the second-generation platform. The company is also exploring different form factors of batteries to enhance versatility.
To extend the driving range further, Hyundai Motor intends to implement technology that enables battery charging and discharging while driving, utilizing an independent power bank. In addition, the integration of an AI-based battery management system will support real-time monitoring and diagnosis of battery conditions, ensuring enhanced safety by avoiding thermal runaway.
In addition to these hardware improvements, the modular architectures and next-generation platform will enable software architecture compatibility in support of Hyundai Motor’s software-defined vehicle (SDV) strategy. The company aims to build an app ecosystem through the application of an open operating system and controller integration, including Level 3 and higher autonomous driving capabilities, high-performance semiconductors and over-the-air (OTA) update advancements.
Production. In expanding production for the electrification transition, Hyundai Motor is not only building new factories dedicated to EVs but it is also promoting a rapid and efficient demand response strategy by utilizing its existing ICE plants.
The proportion of global EV production is set to increase from 8% this year to 34% in 2030. The company plans to expand production by region through a two-track approach of line conversion in ICE factories and new dedicated EV plant establishment.
Since the demand for ICE vehicles remains high, the company is currently producing EVs on mixed production lines as it is more cost efficient than building more EV-dedicated factories. By utilizing existing lines, construction time is much shorter than building new plants and can be ramped up quickly to meet EV demand.
The company is currently producing EVs in this way at its plants in the US, South Korea, the Czech Republic, and India. It plans to convert additional lines as market demand dictates.
In addition, the company is building dedicated EV factories in regions that are expected to grow significantly in the future and require localization. The new factories will be equipped with new smart factory technologies to maximize the efficiency of EV production.
Hyundai’s first dedicated EV factory, the Hyundai Motor Group Metaplant America (HMGMA) in Georgia, is under construction with a targeted start-up date in the second half of 2024, with an annual production capacity of 300,000 vehicles to meet the demand for EVs in North America. Meanwhile, an EV-dedicated factory in Korea, which is being established with an investment of about KRW 2 trillion (US$1.6 billion), aims to start mass production in 2025, responding not only to domestic demand for EVs but also to the rapidly growing global market.
To maximize production efficiency at these dedicated EV factories, Hyundai Motor Group Innovation Center in Singapore (HMGICS), which is scheduled to be operational this year, will be equipped with smart factory technology. HMGICS will demonstrate various new manufacturing technologies for enhancement of quality, logistics and management automation and others.
The company will apply the smart manufacturing platform to factories dedicated to EVs. HMGMA will adopt more than 75% of the new technologies demonstrated at HMGICS. Compared to Hyundai Motor’s plant in Montgomery, Alabama, the company expects to improve logistics and assembly automation rates significantly and the number of vehicles that can be produced.
In the US market, Hyundai Motor plans to increase the localization rate by increasing the proportion to 75% from the current 0.7%. In Europe, it will also promote electrification in line with market conditions by increasing the proportion to 54% from the current 7%. The company plans to increase the proportion of EV production in other regions to 16% from the current 2%.
With global EV demand growing faster than market forecasts, Hyundai Motor is raising its 2030 sales target from 1.87 million units to 2 million units. The company has also raised sales targets for major regions and is preparing to flexibly adjust its sales targets according to market demand.
Hyundai Motor is targeting more than 10% profitability for EVs in 2030 based on the EV development system implemented by the IMA, high-margin derivative model operation, cost reduction through production facility operations strategy and new revenue generation through SDVs.
Batteries. Given the importance of EVs to the Hyundai Motor Way strategy, Chang Hwan Kim, SVP and Head of the Battery Development Center, detailed the company’s advancing development capabilities to improve battery performance continuously and to strengthen price competitiveness.
For its battery-wise competitiveness, Hyundai Motor plans to invest KRW 9.5 trillion (US$7.4 billion) over the next 10 years. The company aims to enhance internal capabilities for battery development, diversify external collaboration and develop next-generation batteries.
Hyundai Motor has established a specialized battery development organization within its Namyang R&D Center, focused on battery system and cell design, battery safety reliability and performance development and next-generation batteries. The company has formed a dedicated organization for each function required for battery development and is securing/training specialized personnel. It is also improving battery performance, developing advanced technologies for next-generation batteries and building infrastructure.
In addition, the company is expanding external collaborations with specialized companies, startups and universities. It is also establishing JVs with battery companies to ensure stable supply and to secure optimized battery performance for its EVs. Joint research and equity investment in startups to accelerate the development of next-generation batteries is also underway.
For solid-state batteries, Hyundai Motor is collaborating with companies, such as Solid Power, to secure elements and manufacturing process technologies and collaborating with SES to develop lithium metal batteries. In addition, the company is internalizing next-generation battery element technology and expanding its talent pool.
Hyundai Motor has completed the construction of the Battery Joint Research Center at Seoul National University, which is scheduled to open in July this year. The dedicated research facility is equipped with the highest specification laboratory equipment at the same level as its own to improve the quality and completeness of its research.
The company is also utilizing these internal and external resources for material sourcing, stabilizing material supply and demand by recycling raw materials, battery cell design and next-generation battery development plans. It is focusing on lithium and nickel, which are essential for electrification, and entering into partnerships to secure these materials. It continues to consult not only with material suppliers but also with domestic and overseas organizations to strengthen the battery material sector.
In addition, to protect the environment and secure sustainable raw materials in the mid- to long-term, Hyundai Motor is safely recovering batteries through collaboration with the Group’s companies. Secure recycling technology to reutilize recycled materials for battery manufacturing will enable the sustainable lifecycle of batteries.
Considering the special properties of automobiles, the company has continuously strengthened its battery design capabilities to achieve a high level of performance. As a result, it has been able to successfully launch EVs with competitive driving ranges and the fastest charging speeds. The hybrid model that will be released this year will be equipped with batteries designed by Hyundai Motor and in collaboration with SK On.
Going forward, the company will continue to ensure superior performance and safety of its batteries and increase cost competitiveness. It is preparing various battery cells optimized for each vehicle type in consideration of the market and customer needs. It plans to introduce competitive lithium-iron-phosphate (LFP) batteries with increased energy density and improved low-temperature efficiency for the first time around 2025. The number of models to be equipped with LFP batteries will be expanded for emerging markets first.
Hyundai Motor is also advancing its battery management capabilities to maximize the performance of EVs so that batteries can operate at high efficiency and safety under optimal conditions. In addition, the company has further advanced the proactive diagnostic function of the battery management system to prevent safety issues through real-time battery condition monitoring.
To realize high energy density and improve battery safety, the company is focusing on the development of next-generation batteries, including lithium metal batteries and solid-state batteries, in the mid- to long-term. Next-generation batteries require the development of not only battery materials and cells, but also equipment and manufacturing technologies for mass production must be developed in parallel.
In order to secure technologies in all areas, the company is conducting multi-faceted collaborations with specialized companies. The aforementioned Hyundai Motor Group-Seoul National University Joint R&D Center is conducting research on next-generation batteries. It is also strengthening internal capabilities to accelerate the development of next-generation batteries by building a next-generation battery research center in Uiwang, Gyeonggi-do, scheduled for completion in 2024.
The company is even considering production verification through a small-scale pilot line. Through this, it will verify the entire value chain technology from securing battery materials, cell design and production to demonstrate the production of next-generation batteries.
The next-generation battery developed in this way will be utilized not only for EVs but also as a power source for future mobility, such as AAM and robotics. It will make a great contribution to increasing synergies between future businesses as a mobility company. By securing the entire battery value chain technology, Hyundai Motor will realize optimized batteries for vehicles, cost competitiveness and consolidate its leadership in the EV era.
Autonomous driving, robotics and AAM.
With Hyundai Motor transforming into a smart mobility solution provider, Heung-soo Kim, EVP and Head of the Global Strategy Office (GSO), provided details of the company’s progress in developing future mobility technologies.
In the field of autonomous driving, an IONIQ 5-based driverless robotaxi business operated by Hyundai Motor Group and Aptiv’s joint venture, Motional, is set to launch in Las Vegas at the end of this year. The Group plans to expand the service globally and lead the autonomous driving market. To this end, Motional is conducting pilot services with Uber and Lyft, the dominant operators in the ride-hailing sector. In particular, it has agreed to cooperate with Uber on an autonomous robotaxi business across the US over the next 10 years.
For the successful commercialization of Motional, the Group will not only develop the vehicle but also the sales network, infrastructure and after-sales service. It will continue to actively engage in manpower exchanges and business collaboration with Motional to secure industry-leading technology and lead the global autonomous driving market.
Hyundai Motor also wants to provide new mobility customer experiences through software-based SDV development, To this end, the company is actively enhancing its software development capabilities by utilizing Hyundai-backed 42dot as a base for its Global Software Center. Since its acquisition in August 2022, 42dot has been playing an integral role in internalizing SDV technology.
42dot will start developing its own software platform called Titan by 2024 and validate the platform by 2026 in order to launch an autonomous driving purpose-built vehicle (PBV) business after 2027 with the aim of turning a profit after 2028, according to a phased technology development roadmap.
With 42dot’s software capabilities and autonomous driving PBV solutions, the Group will continue to develop new businesses based on software innovation in the mobility/logistics sector.
Having acquired Boston Dynamics in 2021 to secure robotics leadership, Hyundai Motor is proceeding with the internalization of core hardware and software through its Robotics Lab. The industrial inspection robot Spot, intelligence logistics robot Stretch and multi-purpose humanoid robot Atlas will continue to strengthen Hyundai Motor’s future competitiveness.
In addition, the Robotics Lab is developing cognitive judgment technology, natural language, spatial navigation and movement, and differentiated mobile platform technology. It is connecting services that create new value for customers through a robot management system, motion-sensing wearable robots MEX, VEX and CEX, and multi-purpose mobile platforms MobED and DAL-e.
The future robotics business will utilize the Group’s existing capabilities in R&D, purchasing, manufacturing and sales, with Boston Dynamics and Robotics Lab as the main players in this expanding business area.
Advanced air mobility (AAM) will be a key technology in the development of future cities. Hyundai Motor Group established Supernal, LLC in Washington, D.C. in 2021 and is developing a full-scale technology model in the near, mid- to long-term, planning pilot-ridden flight tests and securing the infrastructure for airframe manufacturing.
In addition, Hyundai Motor is working with Microsoft, aircraft engine manufacturer Rolls-Royce, KT, Hyundai Engineering and Construction as well as other Korean and foreign partners in the telecommunications and construction sectors to expand into various related businesses. Through these efforts, the company expects to lead the way in building the entire AAM ecosystem.
Hydrogen. Hyundai Motor Group aims to secure a new growth axis by building a hydrogen energy ecosystem at the Group level. The Group plans to build a ‘Mobilize Energy’ toolbox for the production of resource-circulating hydrogen and manufacturing of green steel in the energy and resources sector, and decarbonization of heat and power sources for business sites through hydrogen. In the utilization sector, it will build hydrogen mobility, fuel cells and accompanying infrastructure, and eco-friendly logistics systems using hydrogen.
The company plans to realize carbon neutrality through the ‘Mobilize Energy’ toolbox, with clean hydrogen, including biogas and waste plastic-based hydrogen, powering its EV production facilities and all the logistics, power generation and infrastructure surrounding them.
By expanding the supply of hydrogen vehicles, the Group will also improve the logistics system at seaports and airports. In addition, as next-generation hydrogen fuel cell technology advances, fuel cell systems will be used to power data centers and other applications.
To achieve this vision, the Group will expand the hydrogen value chain based on cooperation among Group affiliates in the global hydrogen market, which is expected to reach KRW 126 trillion (US$97.8 billion) in 2030 and KRW 250 trillion (US$194 billion) in 2050.
The Group plans to present more on its hydrogen business vision and strategy at 2024 CES. It will continue to share the status of other future technologies announced by the GSO with investors.

Uranium Exploration Company Announces Additional Staking in the Athabasca Basin
Source: Streetwise Reports 12/22/2023
Skyharbour Resources Ltd. announced an update from its Canada-based Falcon Project along with additional…
Tesla Launches New Mega Factory Project In Shanghai, Designed To Manufacture 10,000 Megapacks Per Year
Tesla Launches New Mega Factory Project In Shanghai, Designed To Manufacture 10,000 Megapacks Per Year
Tesla has launched a new mega factory…
Giving thanks and taking stock after “a remarkable year”
An end-of-year thank you to our readers, industry colleagues and advertisers before Electric Autonomy breaks from publishing until Jan. 2
The post Giving…