Economics
The Fed Squeeze v. The Market Ease
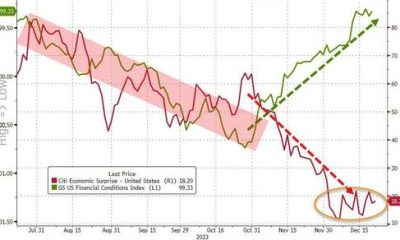
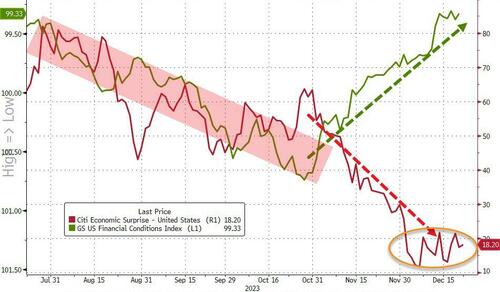
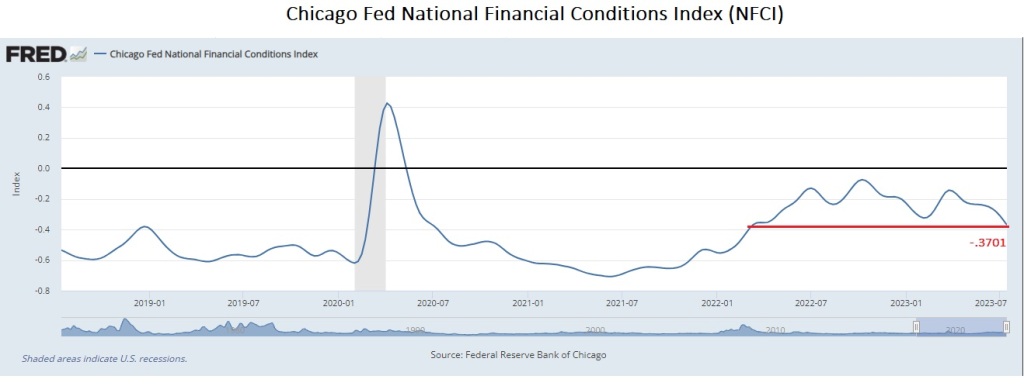
We are amazed that even after over 500 bps of policy rate increases, financial conditions, as measured by the Chicago Fed’s NFCI, are as loose as they…
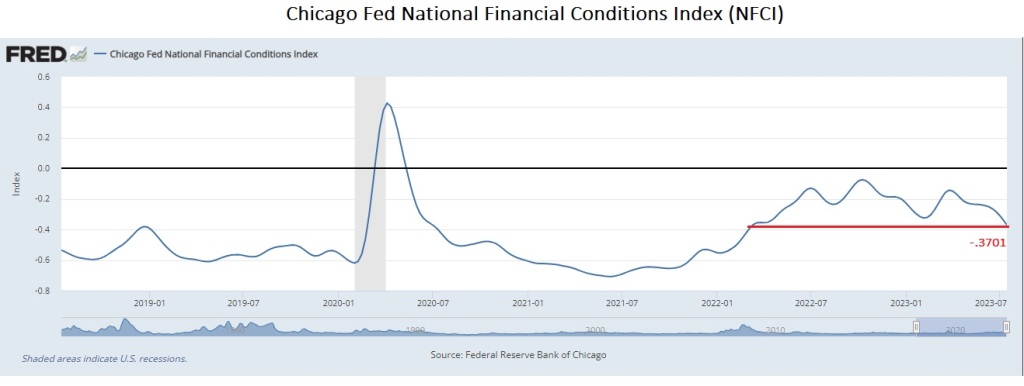
We are amazed that even after over 500 bps of policy rate increases, financial conditions, as measured by the Chicago Fed’s NFCI, are as loose as they were back in March 2022, when the Fed Funds rate was around 25 bps.
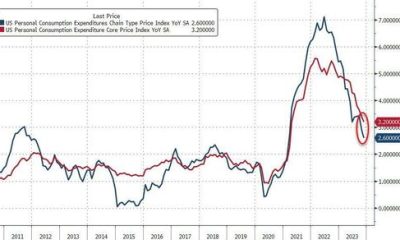
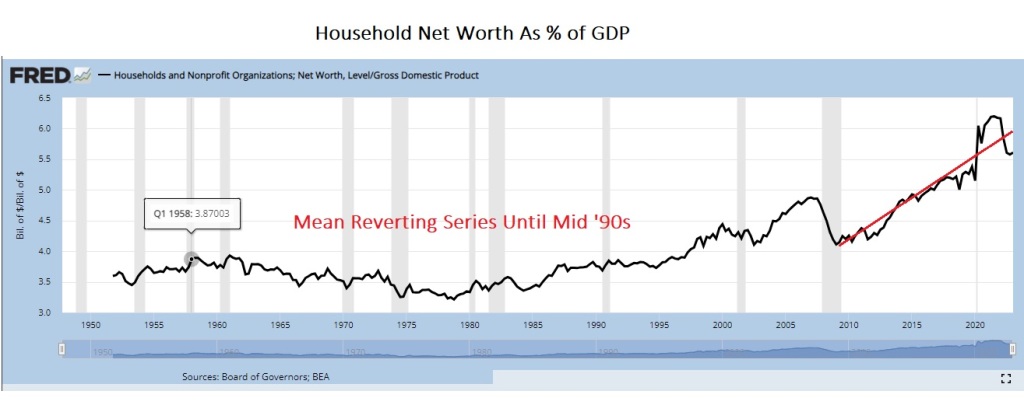
It’s also quite surprising that household wealth, our preferred “loose” measure of the aggregate “money” supply stock, is turning up again. We estimate the current level is around 5.8x nominal GDP. In theory, this metric should be mean reverting as it was for almost fifty years before the mid-1990s.
Our priors are globalization, technological advances, China and Eastern European labor forces entering the global labor market, among other things, have hallowed U.S. aggregate demand, and the Fed has been forced to use monetary policy, primarily through quantitative easing, to inflate asset prices above historical norms to keep demand above the waterline.
Furthermore, our working hypothesis is that the Fed’s inflated balance sheet still supports the asset markets and keeps household wealth, which is grossly skewed to the top 10 percent of households, at extreme levels driven by the emergency COVID monetary injections. At some point, quantitative tightening will begin to bite the asset markets. Thus far, however, they have yet to be chastened.
Upshot = Hawkish Fed
The Fed is going to have to remain hawkish, as they even understand that “wealth without work” or production is one of the deadly sins of monetary policy, which was painfully discovered during the past few years.
We wouldn’t be surprised to hear Chairman Powell express his frustrations and highlight, in red, the easing of monetary conditions, which is a headwind to the Fed’s effort to slow aggregate demand, at the FOMC meeting this week. Wait for it.
Alan Greenspan had a similar dilemma in the mid-aughts, which he labeled the bond market conundrum, where the yield curve wouldn’t cooperate with the Fed’s tightening cycle, which allowed the housing and credit bubble to continue to expand. Monetary policymakers were forced to keep tightening until the markets and the economy broke.
As always, we are contrarian and reserve the right to be wrong, as we often are, but still freaking love the thought experiment.

Argentina Is One of the Most Regulated Countries in the World
In the coming days and weeks, we can expect further, far‐reaching reform proposals that will go through the Argentine congress.
Crypto, Crude, & Crap Stocks Rally As Yield Curve Steepens, Rate-Cut Hopes Soar
Crypto, Crude, & Crap Stocks Rally As Yield Curve Steepens, Rate-Cut Hopes Soar
A weird week of macro data – strong jobless claims but…
Fed Pivot: A Blend of Confidence and Folly
Fed Pivot: Charting a New Course in Economic Strategy Dec 22, 2023 Introduction In the dynamic world of economics, the Federal Reserve, the central bank…